Diabetic Retinopathy
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy occurs when high blood sugar levels cause damage to blood vessels in the retina.
Diabetic retinopathy occurs when high blood sugar levels cause damage to blood vessels in the retina.

The symptoms of diabetic retinopathy often don’t appear until major damage occurs inside of the eye. They include
The longer a person has diabetes, the more likely he or she is to develop diabetic retinopathy, particularly if the diabetes is poorly controlled.
other medical conditions like high blood pressure and high cholesterol increase the risk
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestates) inside a woman’s uterus (womb).
Is normally defined as the method by which an offspring acquires predisposed characteristics from its parent cell.
A lifestyle with a lot of sitting and lying down, with very little to no exercise.
The sum of food consumed by a person or other organism.
A complex disease involving an excessive amount of body fat.
If you are diagnosed with diabetes, it is important to do the following:
If you or someone close to you has developed diabetic retinopathy, do not put off an eye test. Walk into Dr. Agarwal’s Eye Hospital for an appointment with top specialists and surgeons in the field of eye care.
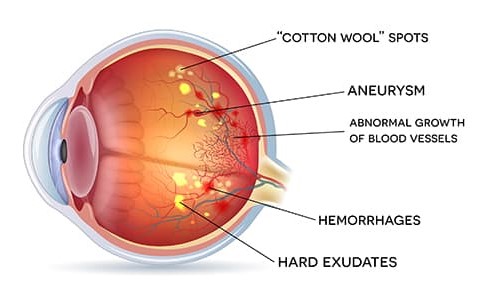
swelling in small areas of the blood vessels in the retina.
some of the blood vessels in the retina will become blocked leading to hemorrhages
more blocked blood vessels, which lead to areas of the retina no longer receiving adequate blood flow
new blood vessels will begin to grow in the retina, but they are fragile and abnormal, hence they can leak blood which will lead to vision loss and possibly blindness.
blood vessels become leaky in the macula which is the central area of the retina which gives us the best visionDiabetic Retinopathy Diagnosis
This measures a person’s vision.
This test measures pressure inside the eye.
Drops placed on the eye’s surface widen the pupil, allowing a physician to examine the retina and optic nerve.
It allows the doctor to check the retina for:
It uses light waves to produce images of the retina to assess the amount of fluid.
During this test, your doctor will inject a dye into your arm, allowing them to track how the blood flows in your eye. They’ll take pictures of the dye circulating inside of your eye to determine which vessels are blocked, leaking, or broken.
Diabetic retinopathy is a diabetes complication that affects the eyes, caused by damage to the blood vessels of the retina.
Symptoms include blurred vision, floaters, difficulty seeing at night, faded colors, and sudden vision loss. Early stages may have no symptoms.
It is diagnosed through a comprehensive eye exam, including a dilated eye exam, optical coherence tomography (OCT), and fluorescein angiography.
Risk factors include having diabetes, poor blood sugar control, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, pregnancy, and long-term diabetes.
Treatment depends on severity and includes managing diabetes, laser surgery, vitrectomy, and injections to reduce inflammation and prevent new blood vessel growth.